Basics
개요
설명
Spring Framework에서 Bean은 어플리케이션을 구성하고, IoC container에 의해 관리되어 지는 객체를 의미한다. Bean은 간단히 말해 IoC container에 의해 객체화되고, 조립되고, 또는 관리되는 객체이다. Bean들과 Bean들간의 종속성은 container가 사용하는 설정 메타데이터에 의해 결정된다.
The container
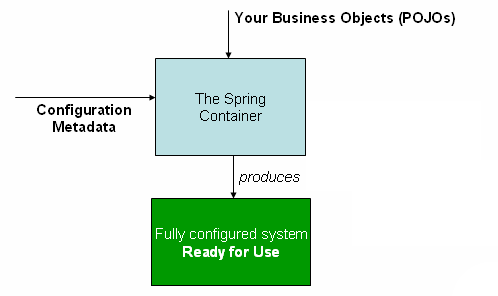
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory 인터페이스는 Spring IoC Container의 핵심 인터페이스이다. Spring IoC Container는 객체를 생성하고, 객체간의 종속성을 이어주는 역할을 한다.
설정 정보(Configuration Metadata)
위 그림에서 보듯이, Spring IoC container는 설정 정보(configuration metadata)를 필요로한다. 이 설정 정보는 Spring IoC container가 “객체를 생성하고, 객체간의 종속성을 이어줄 수 있도록” 필요한 정보를 제공한다. 설정 정보는 일반적으로 XML 형태로 작성된다. 설정 정보는 XML 형태가 아닌 Java Annotation을 이용하여 설정이 가능하다. Annotation을 사용한 설정 방법은 Annotation-based configuration에서 설명하고 있다.
아래 예제는 XML 형태의 설정 정보의 기본적인 모습이다.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd"> <bean id="..." class="..."> <!-- collaborators and configuration for this bean go here --> </bean> <bean id="..." class="..."> <!-- collaborators and configuration for this bean go here --> </bean> <!-- more bean definitions go here --> </beans>
<beans> tag는 Spring IoC container의 설정 정보를 나타내는 tag이다. 그리고 각각의 <bean> tag는 Spring IoC container가 생성하고, 관리할 객체의 정의를 나타낸다.
XML 설정 정보를 여러 개의 파일로 나뉘어 구성될 수 있다. 이 경우, 전체 설정 정보를 읽기 위해서 하나의 설정 파일에서 다른 파일을 import할 수 있다. Import 하는 방법으로 <import> tag를 사용한다.
<beans> <import resource="services.xml"/> <import resource="resources/messageSource.xml"/> <import resource="/resources/themeSource.xml"/> <bean id="bean1" class="..."/> <bean id="bean2" class="..."/> </beans>
<import> tag의 resource attribute는 import할 XML 설정 파일의 위치를 나타낸다.
Container 객체화
다음은 Container를 객체화하는 한 예이다.
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( new String[] {"services.xml", "daos.xml"}); // an Application is also a BeanFactory (via inheritance) BeanFactory factory = context;
위 예제의 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext는 ApplicationContext의 한 종류이며, ApplicationContext 인터페이스는 BeanFactory 인터페이스를 상속하고 있다.
Container 사용 방법
Container를 객체화하면 getBean(String) 메소드를 사용하여 bean을 가져올 수 있다.
The beans
Spring IoC container는 다수의 bean들을 관리한다. Container는 설정 정보를 사용하여 bean들은 생성한다. Container에서 사용하는 bean 정의는 아래 정보를 담고 있다.
- 클래스 이름(a package-qualified class name): bean의 실제 구현 클래스를 나타낸다.
- Bean 행동 정보(bean behavioral configuration elements): container 안에서 bean이 어떤 식으로 행동하는지에 대한 정보를 나타낸다.(scope, lifecycle callbacks 등등)
- 다른 bean에 대한 참조(references to other beans): bean이 동작하기 위해 필요한 다른 bean들에 대한 참조 정보를 나타낸다. 이런 참조는 협력자(collaborators) 또는 종속성(dependencies)라고도 한다.
- 기타 객체에 설정할 정보들(other configuration settings): connection pool을 관리하는 bean에서 사용할 connection의 개수, 또는 pool의 최대 크기 등
위 개념적인 정보들은 실제 <bean> tag로 작성된다. <bean> tag를 구성하는 bean 정의는 아래 표와 같다.
| Feature | Explained in… |
|---|---|
| class | Bean 객체화(Instantiation beans) |
| name | Bean 이름(Naming beans) |
| scope | Bean scope |
| constructor arguments | 종속성 삽입(Injecting dependencies) |
| properties | 종속성 삽입(Injecting dependencies) |
| autowiring mode | 자동엮기(Autowiring collaborators) |
| dependency checking mode | 종속성 검사(Checking for dependencies) |
| lazy-initialization mode | 늦은 객체화(Lazily-instantiated beans) |
| initialization method | 객체화 callbacks(Initialization callbacks) |
| destruction method | 파괴 callbacks(Destruction callbacks) |
Bean 이름(Naming beans)
모든 bean은 하나 이상의 id를 가져야 하며, 각각의 id는 container안에서 단 하나만 존재해야 한다. 일반적으로 대부분의 bean은 하나의 id를 가지지만, 별명(alias)를 사용하여 둘 이상의 id를 가질 수도 있다.
Bean id에 대한 명명 규칙은 Java의 class field 명명 규칙과 같다. id는 소문자로 시작하고, 두번째 단어부터는 첫글자는 대문자로 작성한다. 'accountManager', 'accountService', 'userDao', 'loginController' 등
Bean 별명(Aliasing beans)
<alias> tag를 사용하여 이미 정의된 bean에게 추가적인 이름을 부여할 수 있다.
<alias name="fromName" alias="toName"/>
name attribute는 대상이 되는 bean의 이름이고, alias attribute는 부여할 새로운 이름이다.
Bean 객체화(Instantiation beans)
모든 bean 정의는 객체화를 위해 실제 Java Class가 필요하다.
XML 설정에서는 'class' attribute를 통해 Java Class를 설정한다. 대부분의 경우 Container는 bean를 객체화하기 위해서 Java의 'new' 연산자를 사용한다. 또는 특수한 경우, static 메소드를 사용할 수도 있다. 본 문서는 생성자를 이용한 객체화만을 설명한다.
생성자를 이용한 객체화는 가장 일반적인 방식으로, 다음과 같이 사용한다.
<bean id="exampleBean" class="example.ExampleBean"/> <bean name="anotherExample" class="examples.ExampleBeanTwo"/>
참고자료
전자정부 표준프레임워크 라이센스(바로가기)
전자정부 표준프레임워크 활용의 안정성 보장을 위해 위험성을 지속적으로 모니터링하고 있으나, 오픈소스의 특성상 문제가 발생할 수 있습니다.
전자정부 표준프레임워크는 Apache 2.0 라이선스를 따르고 있는 오픈소스 프로그램입니다. Apache 2.0 라이선스에 따라 표준프레임워크를 활용하여 발생된 업무중단, 컴퓨터 고장 또는 오동작으로 인한 손해 등에 대해서 책임이 없습니다.